
FOTIVDA® (tivozanib) mechanism of action

FOTIVDA is a potent and selective triple vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) inhibitor with a long half-life1*
- Highly vascular tumors in clear cell rrRCC demand VEGFR inhibition2
- Less selective VEGFR TKIs inhibit a range of other kinases3
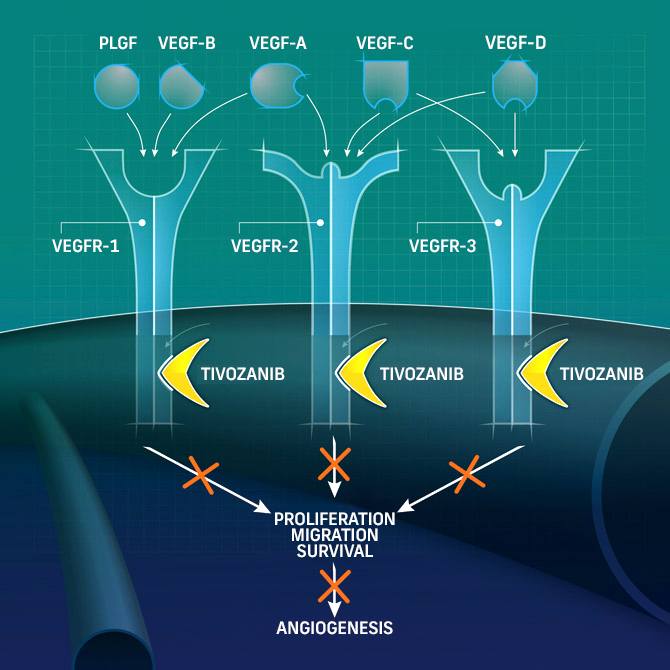
VEGFR 1, 2, 3 enables1:
- Angiogenesis
- Tumor growth
- Progression
Tivozanib inhibits1*:
- Phosphorylation of VEGFR 1, 2, 3
Leading to a reduction in1‡:
- Angiogenesis
- Vascular permeability
- Tumor growth
*In vitro.1
†In human RCC in tumor xenograft models.1
What is the mechanism of action for FOTIVDA® (tivozanib)?
FOTIVDA® (tivozanib) is a highly potent, selective VEGF receptor inhibitor with a long half-life, enabling sustained suppression of tumor blood vessel growth in metastatic RCC while limiting off-target effects.
Watch Dr. Barata to learn more about the mechanism of action for tivozanib.
What is the benefit of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibition for treatment of refractory renal cell carcinoma (RCC)?
The benefit of inhibiting the VEGF pathway—especially with TKIs—is the ability to reduce the tumor’s blood supply, slowing disease progression, which can be effective in refractory cases.
Watch Dr. Barata to learn more about the mechanism of action for tivozanib.
Explore the importance of VEGFR in previously treated patients.
Reach out to an AVEO Oncology Account Manager.
RCC=renal cell carcinoma; rrRCC=relapsed/refractory renal cell carcinoma; TKI=tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
References: 1. FOTIVDA (tivozanib) [package insert]. Boston, MA: AVEO Pharmaceuticals, Inc, January 2025. 2. Makhov P, Joshi S, Kutikov A, et al. Resistance to systemic therapies in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: mechanisms and management strategies. Mol Cancer Ther. 2018;17(7):1355-1364. 3. Albiges L, Barthelemy P, Gross-Goupil M, Negrier S, Needle MN, Escudier B. TiNivo: safety and efficacy of tivozanib-nivolumab combination therapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Annals Oncol. 2021;32(1):97-102.
INDICATIONS
FOTIVDA is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) following two or more prior systemic therapies.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypertension was reported in 45% of patients (22% ≥ Grade 3). Hypertensive crises were reported in 0.8% of patients. Do not initiate FOTIVDA in patients with uncontrolled hypertension. Monitor for hypertension and treat as needed. Reduce the FOTIVDA dose for persistent hypertension not controlled by anti-hypertensive medications. Discontinue FOTIVDA for severe hypertension that cannot be controlled with anti-hypertensive therapy or for hypertensive crisis.
INDICATIONS
FOTIVDA is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) following two or more prior systemic therapies.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypertension was reported in 45% of patients (22% ≥ Grade 3). Hypertensive crises were reported in 0.8% of patients. Do not initiate FOTIVDA in patients with uncontrolled hypertension. Monitor for hypertension and treat as needed. Reduce the FOTIVDA dose for persistent hypertension not controlled by anti-hypertensive medications. Discontinue FOTIVDA for severe hypertension that cannot be controlled with anti-hypertensive therapy or for hypertensive crisis.
Cardiac failures were reported in 1.6% of patients (1% ≥ Grade 3); 0.6% of events were fatal. Monitor for signs or symptoms of cardiac failure during treatment with FOTIVDA. Manage with dose interruption, dose reduction, or discontinuation.
Cardiac ischemia were reported in 3.2% of patients; 0.4% of events were fatal. Arterial thromboembolic events were reported in 2.0% of patients, including death due to ischemic stroke (0.1%). Closely monitor patients at risk for, or who have a history of these events. Discontinue FOTIVDA in patients who develop severe arterial thromboembolic events, such as myocardial infarction and stroke.
Venous Thrombotic Events (VTE) were reported in 2.4% of patients, including 0.3% fatal events. Closely monitor patients who are at increased risk for these events. Discontinue in patients who develop serious VTEs.
Hemorrhagic Events were reported in 11% of patients; 0.2% of events were fatal. Use FOTIVDA with caution in patients who are at risk for or who have a history of bleeding.
Proteinuria was reported in 8% of patients (2% = Grade 3). Monitor during treatment with FOTIVDA. For moderate to severe proteinuria, reduce the dose or interrupt treatment. Discontinue in patients who develop nephrotic syndrome.
Gastrointestinal (GI) Perforation including fatal cases, has been reported in patients receiving FOTIVDA. Monitor for symptoms of GI perforation or fistula formation periodically throughout treatment with FOTIVDA. Permanently discontinue FOTIVDA in patients who develop severe or life-threatening GI perforation.
Thyroid Dysfunction events were reported in 11% of patients (0.3% ≥ Grade 3). Monitor thyroid function before and during treatment with FOTIVDA.
Wound Healing Complications: Withhold FOTIVDA for at least 24 days prior to elective surgery and do not administer for at least 2 weeks after major surgery and until adequate wound healing is observed.
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS) can occur with FOTIVDA. Evaluate for RPLS in patients presenting with seizures, headache, visual disturbances, confusion, or altered mental function. Discontinue if signs or symptoms of RPLS occur.
Embryo-fetal Toxicity: FOTIVDA can cause fetal harm. Advise patients of the potential risk to a fetus, to avoid becoming pregnant and to use contraception during treatment and for one month after the last dose of FOTIVDA. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for one month after the last dose of FOTIVDA.
Allergic Reaction to Tartrazine: FOTIVDA 0.89 mg capsule contains FD&C Yellow No. 5 (tartrazine) which may cause allergic-type reactions (including bronchial asthma) in certain susceptible patients.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Common adverse reactions include fatigue/asthenia, hypertension, diarrhea, decreased appetite, nausea, dysphonia, hypothyroidism, cough, and stomatitis.
Serious adverse reactions include bleeding (3.5%), venous thromboembolism (3.5%), arterial thromboembolism (2.9%), acute kidney injury (2.3%), and hepatobiliary disorders (2.3%).
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Avoid coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment and for at least 1 month after the last dose.
The recommended dosage for patients with end-stage renal disease has not been established.
Reduce the FOTIVDA dose for patients with moderate hepatic impairment. The recommended dosage in patients with severe hepatic impairment has not been established.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact AVEO Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-833-FOTIVDA (1-833-368-4832) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Please see full Prescribing Information for FOTIVDA® (tivozanib).

